FOOD ALLERGIES CAUSING INSOMNIA
“A 65-year-old woman suffered from insomnia for 35 years. Upon questioning her, it was discovered that she was allergic to vitamin C. She ate an apple, banana, or orange every night before she went to bed. The allergy kept her awake almost the entire night.”
– Dr Devi Nambudripid
Insomnia Epidemic Grips City
Dubai’s 24/7 lifestyle is causing residents to lose sync with their body clock, resulting in deadly diseases, job losses and even road mishaps. Are you one of them? Here’s a wake-up call.
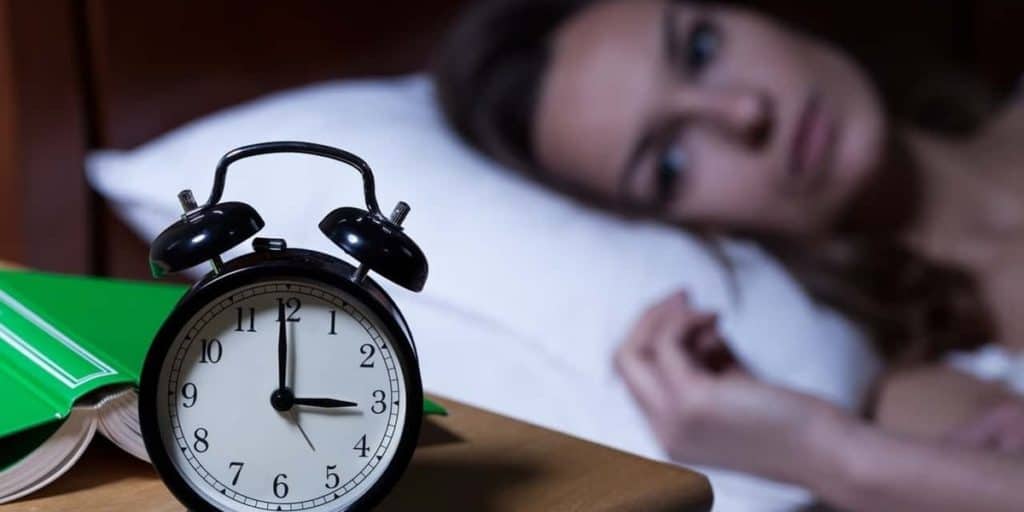

(Source: Gulf News, Published: September 22, 2011, By Faisal Masudi, Staff Report)
Dubai: For long Dubai has prided itself as a city that never sleeps. And now it’s paying a price for it. Dubai is in the grip of an insomnia epidemic as a vast majority of residents cannot afford a good night’s sleep. A survey showed that 68 per cent of UAE residents do not notch up enough hours of slumber. Experts reckon the statistics could be much higher for Dubai, given its frenetic pace of life.
Sleep disorders are behind car accidents, job sackings and even divorces. They are also linked to deadly illnesses like heart disease, hypertension and diabetes.
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by having difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Some people with insomnia may fall asleep easily but wake up too soon. Other people may have the opposite problem or have difficulty with both falling asleep and staying asleep. The end result is poor-quality sleep and the feeling of being unrefreshed.
There are two types of insomnia based on the regularity and duration of the sleep disturbance and daytime symptoms:
- Short-term insomnia: This type of brief insomnia lasts for up to three months. It occurs in 15 to 20 per cent of people.
- Chronic insomnia: This type of insomnia occurs at least three times per week and lasts for at least three months. About 10 per cent of people have chronic insomnia.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Insomnia?
The main symptom of insomnia is trouble falling and/or staying asleep, which leads to lack of sleep. The lack of sleep can cause other symptoms, such as:
- Waking up feeling tired or not well rested
- Feeling tired or very sleepy during the day
- Having trouble focusing on tasks
- Feeling anxious, depressed, or irritable
What Causes Insomnia?
Insomnia may be the primary problem, or it may be associated with other conditions.
Chronic insomnia is usually a result of stress, life events or habits that disrupt sleep. Treating the underlying cause can resolve insomnia, but sometimes it can last for years.
Common causes of chronic insomnia include:
Stress. Concerns about work, school, health, finances or family can keep your mind active at night, making it difficult to sleep. Stressful life events or trauma — such as the death or illness of a loved one, divorce, or a job loss — also may lead to insomnia.
Travel or work schedule. Your circadian rhythms act as an internal clock, guiding such things as your sleep-wake cycle, metabolism and body temperature. Disrupting your body’s circadian rhythms can lead to insomnia. Causes include jet lag from travelling across multiple time zones, working a late or early shift, or frequently changing shifts.
Poor sleep habits. Poor sleep habits include an irregular bedtime schedule, naps, stimulating activities before bed, an uncomfortable sleep environment, and using your bed for work, eating or watching TV. Computers, TVs, video games, smartphones or other screens just before bed can interfere with your sleep cycle.
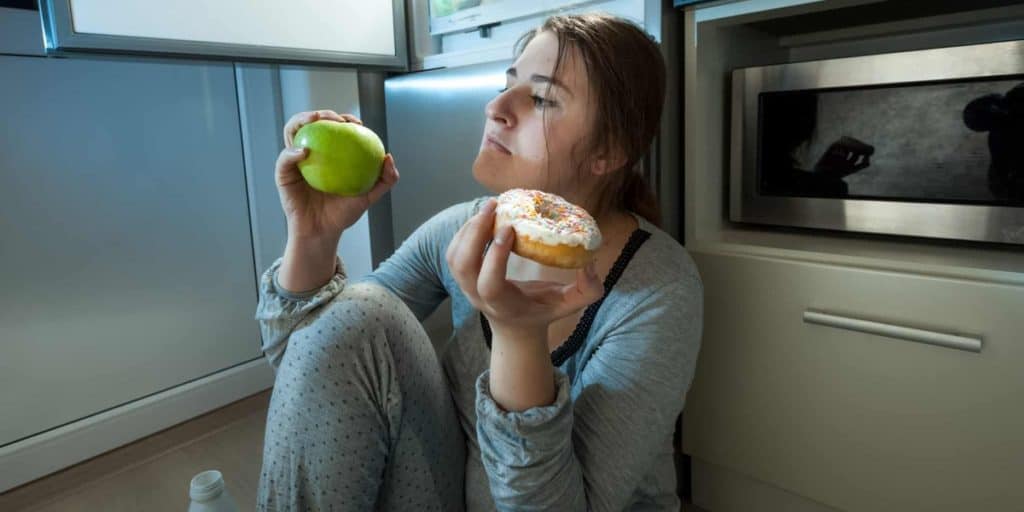

Eating too much late in the evening. Having a light snack before bedtime is OK, but eating too much may cause you to feel physically uncomfortable while lying down. Many people also experience heartburn, a backflow of acid and food from the stomach into the oesophagus after eating, which may keep you awake.
Causes of Short term insomnia can include:
- Food Allergies or Intolerance
- Significant life stress (job loss or change, the death of a loved one, divorce, moving)
- Illness
- Emotional or physical discomfort
- Environmental factors like noise, light, or extreme temperatures (hot or cold) that interfere with sleep
- Some medications (for example those used to treat colds, allergies, depression, high blood pressure, and asthma) may interfere with sleep
- Interferences in normal sleep schedule (jet lag or switching from a day to night shift, for example)
Medical Causes of Insomnia
There are many medical conditions (some mild and others more serious) that can lead to insomnia. In some cases, a medical condition itself causes insomnia, while in other cases, symptoms of the condition cause discomfort that can make it difficult for a person to sleep.
Examples of medical conditions that can cause insomnia are:
- Nasal/sinus allergies
- Gastrointestinal problems such as reflux
- Endocrine problems such as hyperthyroidism
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease
- Chronic pain
- Low back pain
Medications such as those taken for the common cold and nasal allergies, high blood pressure, heart disease, thyroid disease, birth control, asthma, and depression can also cause insomnia.
Insomnia & Food
Certain substances and activities, including eating patterns, can contribute to insomnia. If you can’t sleep, review the following lifestyle factors to see if one or more could be affecting you:
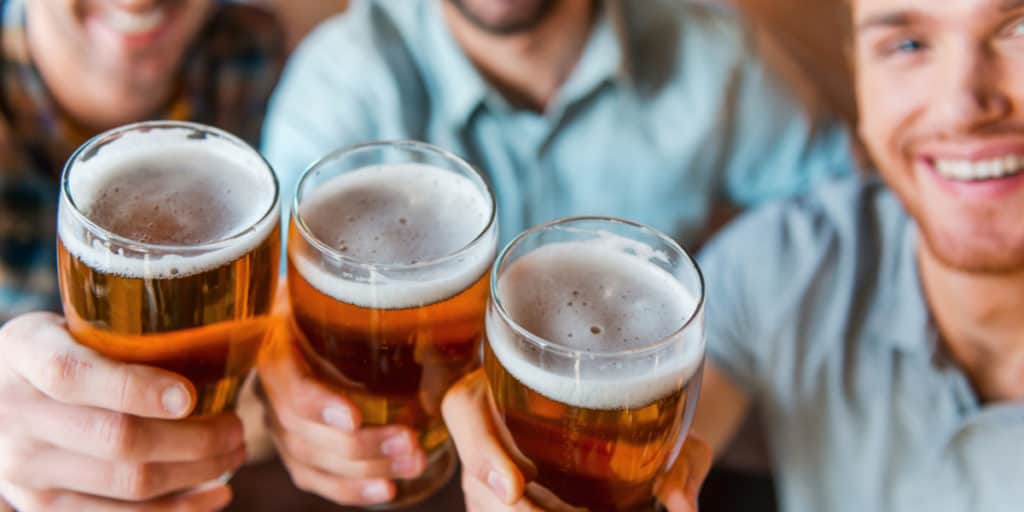

Alcohol is a sedative. It can make you fall asleep initially but may disrupt your sleep later in the night.
Caffeine is a stimulant. Most people understand the alerting power of caffeine and use it in the morning to help them start the day and feel productive. Caffeine in moderation is fine for most people, but excessive caffeine can cause insomnia.
A 2005 National Sleep Foundation poll found that people who drank four or more cups/cans of caffeinated drinks a day were more likely than those who drank zero to one cup/cans daily to experience at least one symptom of insomnia at least a few nights each week.
Caffeine can stay in your system for as long as eight hours, so the effects are long-lasting. If you have insomnia, do not consume food or drinks with caffeine too close to bedtime.
Nicotine is also a stimulant and can cause insomnia. Smoking cigarettes or tobacco products close to bedtime can make it hard to fall asleep and to sleep well through the night. Smoking is damaging to your health. If you smoke, you should stop.
Heavy meals close to bedtime can disrupt your sleep. The best practice is to eat lightly before bedtime. When you eat too much in the evening, it can cause discomfort and make it hard for your body to settle and relax. Spicy foods can also cause heartburn and interfere with your sleep.
Insomnia & Anxiety
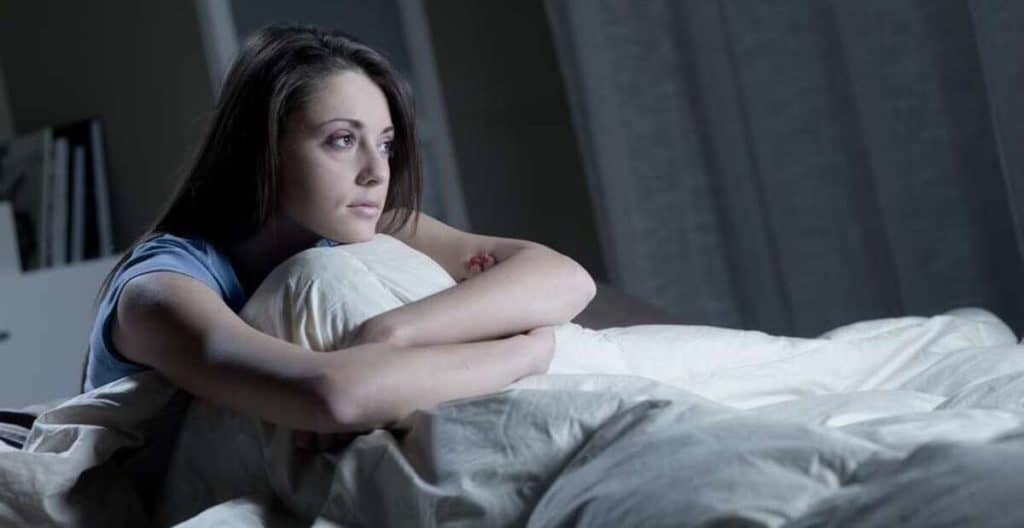

Most adults have had some trouble sleeping because they feel worried or nervous, but for some, it’s a pattern that interferes with sleep on a regular basis. Anxiety symptoms that can lead to insomnia include:
- Tension
- Getting caught up in thoughts about past events
- Excessive worrying about future events
- Feeling overwhelmed by responsibilities
- A general feeling of being revved up or overstimulated
It’s not hard to see why these symptoms of general anxiety can make it difficult to sleep. Anxiety may be associated with onset insomnia (trouble falling asleep), or maintenance insomnia (waking up during the night and not being able to return to sleep). In either case, the quiet and inactivity of the night often bring on stressful thoughts or even fears that keep a person awake.
When this happens for many nights (or many months), you might start to feel anxiousness, dread, or panic at just the prospect of not sleeping. This is how anxiety and insomnia can feed each other and become a cycle that should be interrupted through treatment.
There are cognitive and mind-body techniques that help people with anxiety settle into sleep, and overall healthy sleep practices that can improve sleep for many people with anxiety and insomnia.
Insomnia & The Brain
In some cases, insomnia may be caused by certain neurotransmitters in the brain that are known to be involved with sleep and wakefulness.
There are many possible chemical interactions in the brain that could interfere with sleep and may explain why some people are biologically prone to insomnia and seem to struggle with sleep for many years without any identifiable cause—even when they follow healthy sleep advice.
Sleep Problems in Children with Autism

Most parents struggle at one time or other to get their children to sleep. Tantrums before bedtime, waking up at night, refusing to fall back asleep are common behaviours in children. If your child is experiencing any of these problems, you are definitely not alone.
All parents intermittently deal with children who have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. These temporary sleep difficulties are normal. However, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) appear to have more ongoing sleep-related difficulties. The number of families affected varies from study to study, but significant sleep problems can occur in 40%—80% of children with ASD.
Sleep is a critical component of health. Although we do not understand all its functions, sleep is essential to growing, to restore our body and immune system and to enhance and solidify memory and learning.
For children with ASD, insufficient sleep appears to impact daytime behaviours, making challenging behaviours worse. In addition, sleeping difficulties for the child lead to sleeping difficulties for parents and sometimes siblings, adding to the stress and challenges of parenting a child who has autism. No one can function at their best when they are sleep deprived.
What Causes Sleep Difficulties in Children with Autism?
The most common reasons for sleep difficulties in all children are environmental influences or inadvertent behavioural shaping. For example, parents may assist a child in falling asleep by rocking or holding them and then placing them in bed while asleep. But when children awake naturally later in the night, they do not have access to the things in their environment that are associated with sleep and so are unable to get back to sleep by themselves.
Another common cause of sleep difficulties is putting a child to sleep in a bedroom where he or she engages in stimulating play activities during the day.
Treatment options for insomnia
Some types of insomnia resolve themselves when the underlying cause is removed or wears off. In general, treating insomnia focuses on determining the cause of sleeping problems. Once identified, this underlying cause can be properly treated or corrected.
In addition to treating the underlying cause of insomnia, both medical and non-pharmacological (behavioural) treatments may be employed as adjuvant therapies.
Non-pharmacological approaches to treating insomnia include:
- Improving “sleep hygiene” – don’t over- or under-sleep, exercise daily, don’t force sleep, try to maintain a regular sleep schedule, avoid caffeine at night, do not smoke, do not go to bed hungry, make sure the environment is comfortable
- Using relaxation techniques – such as meditation and muscle relaxation
- Cognitive therapy – one-on-one counselling or group therapy
- Stimulus control therapy – only go to bed when sleepy, refrain from TV, reading, eating, or worrying in bed, set an alarm for the same time every morning (even weekends), avoid long daytime naps
- Sleep restriction – decrease the time spent in bed and partially deprive your body of sleep so you are more tired the next night.
Medical treatments for insomnia include:
- Prescription sleeping pills (often benzodiazepines)
- Antidepressants
- Over-the-counter sleep aids
- Antihistamines
- Melatonin
- Ramelteon
- Valerian Officinalis.
How many hours of sleep do you need?

According to the National Institutes of Health, the average adult sleeps less than seven hours per night. In today’s fast-paced society, six or seven hours of sleep may sound pretty good. In reality, though, it’s a recipe for chronic sleep deprivation.
| Average Sleep Needs by Age | |
| Newborn to 2 months old | 12 – 18 Hrs |
| 3 months to 1 year old | 14 – 15 Hrs |
| 1 to 3 years old | 12 – 14 Hrs |
| 3 to 5 years old | 11 – 13 Hrs |
| 5 to 12 years old | 10 – 11 Hrs |
| 12 to 18 years old | 8.5 – 10 Hrs |
| Adults (18+) | 7.5 – 9 Hrs |
Myths and Facts about Sleep
Myth 1: Getting just one hour less sleep per night won’t affect your daytime functioning.
Fact: You may not be noticeably sleepy during the day, but losing even one hour of sleep can affect your ability to think properly and respond quickly. It also compromises your cardiovascular health, energy balance, and ability to fight infections.
Myth 2: Your body adjusts quickly to different sleep schedules.
Fact: Most people can reset their biological clock, but only by appropriately timed cues—and even then, by one or two hours per day at best. Consequently, it can take more than a week to adjust after traveling across several time zones or switching to the night shift.
Myth 3: Extra sleep at night can cure you of problems with excessive daytime fatigue.
Fact: The quantity of sleep you get is important, sure, but it’s the quality of your sleep that you really have to pay attention to. Some people sleep eight or nine hours a night but don’t feel well rested when they wake up because the quality of their sleep is poor.
Myth 4: You can make up for lost sleep during the week by sleeping more on the weekends.
Fact: Although this sleeping pattern will help relieve part of sleep debt, it will not completely make up for the lack of sleep. Furthermore, sleeping later on the weekends can affect your sleep-wake cycle so that it is much harder to go to sleep at the right time on Sunday nights and get up early on Monday mornings.
Insomnia Treatment without Medicine
With us, we get to the root of the problem, identifying and eliminating the allergen that is causing the recurring symptoms.
We offer the prospect of relief to those who suffer from addiction and allergies by reprogramming the brain to perfect health. Just like rebooting a computer, we can reboot our nervous system to overcome the adverse reactions of brain and body.
To fully understand our techniques, one needs to know some Oriental medical principles. We have taken the acupuncture and Oriental medical theories and developed a technique that can eliminate the reaction from the root.
Addictions can definitely cause illness. Continuous contact with an allergen produces toxins in the body and causes blockages in the meridians. If these blockages are not cleared, reactions to the allergens often produce symptoms that mimic other diseases.
MRT (Muscle Response Testing)
By clearing food and environmental and chemical allergens from the protocol, we strengthen the immune system, eliminate the Physiological blockage the root cause of Insomnia and in bonus, it also helps improve your digestion and absorption. This allows the body to get the necessary nutrients, which are essential for life.
One allergen is cleared per visit. Each individual has a different genetic makeup and health history so the number of sessions required varies from one individual to another. For some people, allergens are cleared immediately however, for others it may take many sessions to accomplish the desired results.
Some people might raise their eyebrows and ask, “Can you really eliminate my Insomnia?” We answer with a resounding “YES!”
Long-Standing Insomnia cleared after treatments
“When I first came to see Dr. Devi, I was only getting 2 1/2 hours to sleep at night because my entire back, arms, neck and head were covered with an itchy rash that I was constantly scratching raw. I couldn’t sleep, I was terrified of eating, and I was despondent. In just a few treatments (basic treatments) the rash started to clear up and, within a week, I was sleeping through the night. What a blessing! I will be forever grateful, and I have gotten better and better.
– Margaret Lespino, Los Angeles, CA
Connect with us through our Facebook page at www.facebook.com/NAETDubai or visit: www.naetdubai.com. You will find a wealth of information here along with an opportunity to speak confidentially through WhatsApp 056-639 0197 or Phone Call 04-420 1633.
You may also email us at admin@naetdubai.com
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]





8 Responses
Thank you 🙂
Hi, thank you for your comment ???? Please don’t forget to subscribe to our blog and you will receive mails once we published new blogs.
Hi, thank you ???? Please don’t forget to subscribe to our blog and you will receive mails once we published new blogs.
Yes, insomnia can treat without medicine. I have treated it with relaxation training. Thanks for sharing the post. This will help people to stop medication and use some other strategies of getting over it.
Thank you for your comment ???? . Please don’t forget to subscribe to our blog and you will receive mails once we published new blogs. Feel free to contact us if you need any further information. Cheers!
Thank you 🙂 We are looking forward to hearing from you on our next blogs.
Thank you 🙂
Thank you 🙂